What is this metric used to assess, and why does its evaluation matter?
This metric quantifies a specific aspect of a process or system. It represents a numerical evaluation, often derived from observed data. For example, it might be a calculation based on the frequency and severity of defects in manufacturing or the accuracy of diagnoses in healthcare. The specific data points contributing to this evaluation depend on the context.
The importance of this evaluation stems from its ability to pinpoint areas requiring improvement and track progress over time. A high score suggests desirable performance levels, while a low score indicates a need for intervention and optimization. Such assessment is crucial for quality control, continuous improvement, and maintaining or enhancing standards of performance. Historical trends in the metric can reveal patterns and shifts that facilitate informed decision-making.
This evaluation is a foundational component for various fields that value efficiency and efficacy. The specific applications are numerous and context-dependent. Subsequent sections of this document will delve deeper into specific scenarios and applications.
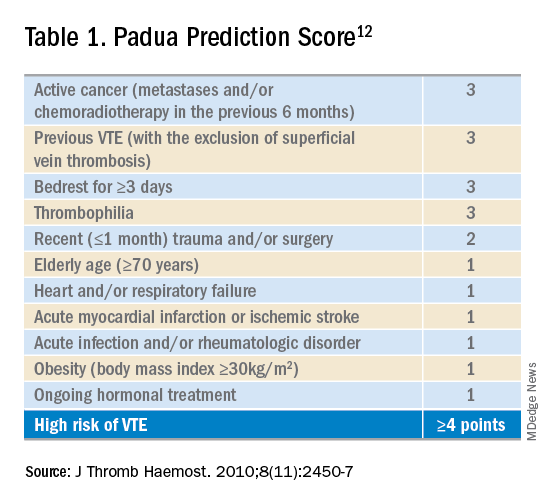
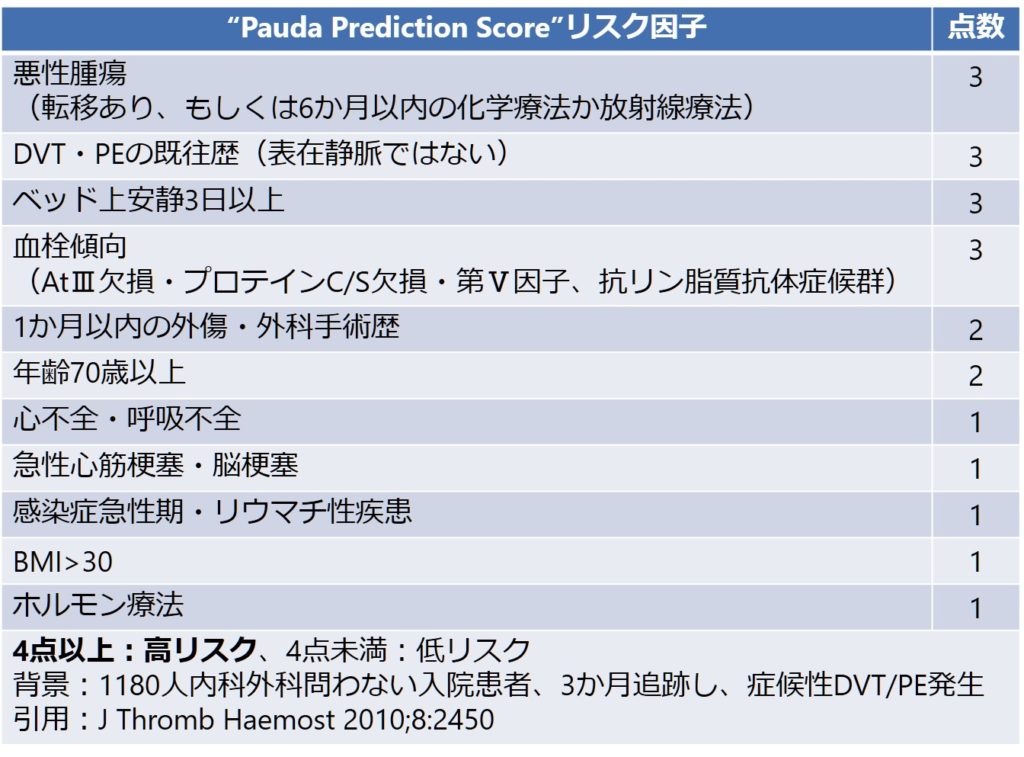
pauda score
Understanding the "pauda score" requires examination of its constituent elements and their combined impact. This metric's significance lies in its ability to assess and quantify performance, informing improvements in various domains.
- Numerical value
- Performance evaluation
- Benchmarking
- Data-driven insights
- Process optimization
- Quality improvement
The "pauda score," as a numerical evaluation, provides a quantifiable measure of performance. Benchmarking against industry standards or internal targets allows for comparison and identification of areas requiring improvement. Data-driven insights derived from the score inform strategic decisions aimed at process optimization. Quality improvement initiatives are then directly tied to the results. This metric becomes a cornerstone for evaluating and enhancing processes, thereby driving consistent, elevated performance. For instance, a high pauda score in manufacturing might indicate high product quality and low defect rates, prompting further exploration for sustaining this level of excellence. Conversely, a low score necessitates investigation into potential sources of error and implementation of corrective measures.
1. Numerical value
The "pauda score" inherently relies on a numerical value to represent performance or a specific characteristic. This numerical aspect is crucial for comparison, benchmarking, and tracking progress. Understanding the nature of this numerical representation allows for a deeper appreciation of the metric's utility and applicability.
- Quantifiable Performance Metrics
The numerical value directly reflects a specific aspect of performance. This could be the percentage of successful transactions, the number of defects in a production run, the accuracy of a diagnosis, or any other relevant measure. The numerical value acts as a precise measure of the target characteristic, facilitating objective assessment.
- Benchmarking and Comparison
Numerical values allow for easy comparison. A high score signifies a favorable performance level, while a low score flags potential areas for improvement. Comparison against industry benchmarks or previous performance data provides context and underscores the significance of the metric.
- Trend Analysis and Predictive Modeling
A series of numerical values, tracked over time, reveals trends and patterns. These trends can be analyzed to predict future performance, identify potential issues, and guide proactive improvements. The numerical value is therefore a key element in proactive management strategies.
- Objective Evaluation and Documentation
Numerical values enable an objective evaluation of the characteristic or process being measured. Documentation of these numerical values is crucial for record-keeping and facilitating subsequent analyses. This objectivity is vital for repeatable processes and robust decision-making.
In essence, the numerical value of the "pauda score" is fundamental to its function as a performance metric. It allows for quantification, comparison, trend analysis, and informed decision-making, contributing to effective management and optimization strategies in diverse fields.
2. Performance evaluation
Performance evaluation is integral to the "pauda score" concept. The score itself is a direct outcome of a performance evaluation process. This process assesses aspects of a system or procedure against predetermined criteria. The "pauda score" then represents a numerical summary of that evaluation. Effective performance evaluation informs the calculation of the score, ensuring a direct correlation between observed performance and the resulting numerical value. Without a robust evaluation process, the "pauda score" loses its meaning and utility as a reliable metric for progress tracking and process optimization.
Consider a manufacturing plant. A meticulous performance evaluation assesses factors like defect rates, production output, and worker efficiency. Data gathered from these evaluations are combined to produce the "pauda score." A consistently high score indicates efficient operations, minimal defects, and productive workflows. Conversely, a low score necessitates investigation into specific areas of inefficiency and implementation of targeted improvements. This direct link between evaluation and the score facilitates a targeted approach to process refinement and ensures that interventions address specific weaknesses identified through the evaluation. Similar methodologies apply in other sectors, like customer service, healthcare, and project management, where performance evaluations underpin the calculation and interpretation of corresponding numerical metrics. In each case, the quality of the evaluation directly impacts the validity and value of the "pauda score" as a tool for assessing and improving performance.
In conclusion, performance evaluation acts as the bedrock upon which the "pauda score" is built. This evaluation process defines the parameters, criteria, and metrics used to arrive at a numerical representation of performance. The validity and practical application of the "pauda score" are inextricably linked to the thoroughness and accuracy of the underlying performance evaluation. Understanding this connection is crucial for utilizing the score effectively to identify areas for improvement and drive meaningful progress in any field where performance measurement is critical.
3. Benchmarking
Benchmarking plays a critical role in interpreting and utilizing the "pauda score." It provides context for understanding performance levels within a specific industry or organizational framework. By comparing performance against established benchmarks, organizations can identify areas for improvement and optimize processes to enhance overall efficiency and effectiveness. The "pauda score," in conjunction with benchmarking, becomes a powerful tool for strategic decision-making and continuous improvement.
- Establishing Performance Standards
Benchmarking establishes standardized performance levels. This allows for a clear understanding of the expected output within the relevant context. For example, a manufacturing company might benchmark their defect rate against industry averages. This comparison sets a standard for acceptable levels of quality. The "pauda score" then provides a measure of how well the specific entity performs against these benchmarks. A consistently high score within the context of the benchmark demonstrates adherence to superior standards. Conversely, a low "pauda score" when compared to the benchmark highlights the need for improvement.
- Identifying Performance Gaps
Comparisons against benchmarks reveal performance gaps. These gaps represent discrepancies between current performance and expected levels. Analyzing these gaps, identified through benchmarking, helps pinpoint areas requiring optimization. For example, if a company's "pauda score" falls significantly below the industry benchmark, the resulting analysis of the gap leads to a comprehensive understanding of the reasons for this underperformance, allowing for targeted interventions.
- Driving Process Optimization
Benchmarking facilitates the identification of best practices. By understanding how high-performing entities achieve their results, companies can adapt successful methodologies and optimize their processes. A "pauda score" aligned with a high-performing benchmark provides valuable insight into the strategic approaches likely driving such outstanding performance, leading to potential process improvements.
- Tracking Progress and Progress Monitoring
Benchmarking supports continuous monitoring of progress. By regularly comparing performance against benchmarks, organizations can track improvements over time. The "pauda score," coupled with the benchmark data, provides a clear view of the progress achieved, thereby indicating the effectiveness of implemented strategies. Regular measurements allow for anticipatory actions and adjustments if performance trends deviate from the target benchmark.
Ultimately, benchmarking, when integrated with the "pauda score," provides a robust framework for performance assessment. This framework, using established industry standards, enables organizations to evaluate their performance objectively and make strategic decisions aimed at continuous improvement.
4. Data-driven insights
Data-driven insights are fundamental to the "pauda score." The score itself is a numerical representation derived from data analysis. Without a robust data collection and analysis process, the "pauda score" lacks meaning and utility as a performance metric. The insights gleaned from data inform the interpretation of the score, revealing patterns and trends that guide improvements in a given system. A high "pauda score" supported by consistent, positive data trends indicates well-optimized processes. Conversely, a low score linked to declining data trends necessitates investigation into factors contributing to this decline.
Consider a manufacturing facility. Data on defect rates, production output, and equipment downtime are meticulously collected and analyzed. This analysis yields insights into potential bottlenecks in production processes. For example, a surge in defects might correlate with a recent equipment malfunction. Identifying this correlation, and using this data to isolate and address the problem, directly improves the "pauda score." This iterative process of data analysisleading to actionable insightsresults in a dynamic and continuously improving system. In healthcare, similar data-driven approaches can identify high-risk patients, optimize treatment plans, and predict hospital readmissions, all contributing to improved patient outcomes and a demonstrably higher "pauda score." In project management, insightful data analysis can predict potential delays, allowing project managers to proactively implement adjustments that maintain a favorable "pauda score." Data-driven insights, therefore, are crucial not just for evaluating performance, but for proactive problem-solving and continuous improvement.
In summary, the "pauda score" relies on data-driven insights for meaning and actionability. Data collection, analysis, and subsequent interpretation are integral to the score's utility. The connection between data-driven insights and the "pauda score" is undeniable. Such understanding underscores the critical need for reliable data collection and rigorous analysis to drive process optimization and achieve desired performance levels in any field where measurement is paramount.
5. Process Optimization
Process optimization is intrinsically linked to the "pauda score." A well-optimized process consistently yields favorable results, reflected in a higher "pauda score." Identifying and implementing improvements within a process directly impacts the numerical value of this metric, ultimately leading to enhanced performance and efficiency. This section examines key aspects of process optimization and its relationship to the "pauda score."
- Identifying Bottlenecks and Inefficiencies
Thorough analysis pinpoints bottlenecks and inefficiencies within a process. This involves detailed examination of each stage, from input to output. For instance, in a manufacturing process, slowdowns at a specific workstation might reveal a bottleneck hindering overall productivity. This identification, achieved through data analysis, is crucial. A "pauda score" reflecting a low performance level directly correlates to a process with significant inefficiencies that must be addressed. Understanding these bottlenecks is paramount to process improvement and ultimately elevates the "pauda score."
- Streamlining Workflow and Procedures
Streamlining workflow involves reorganizing procedures to remove redundancies and unnecessary steps. This could include automating certain tasks or re-allocating responsibilities. For instance, a redundant step in a customer order fulfillment process can be eliminated, accelerating order processing. By streamlining and optimizing the workflow, the "pauda score" improves as the process becomes more efficient and effective. Redundant steps and inefficiencies directly translate into a lower "pauda score." Reducing friction through optimized workflows enhances the metric significantly.
- Leveraging Technology and Automation
Modern technologies and automation often significantly enhance process efficiency and reduce error rates. Implementation of automation in various stages of a process, whether in data entry, manufacturing, or customer service, minimizes human error and accelerates operations. Improved efficiency results in a higher "pauda score." The effectiveness of technologies in streamlining a process directly impacts the numerical value of the metric. Organizations can use this relationship to gauge the success of their technology integrations in a process.
- Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Ongoing monitoring and evaluation are essential for a dynamic optimization process. By tracking performance indicators, analyzing trends, and adapting to changes, organizations can maintain a high "pauda score." This proactive approach allows for timely adjustments to processes based on real-time feedback, ensuring consistent improvement. The ongoing evaluation tied to a "pauda score" provides a mechanism for continual assessment and adjustment of processes for sustained high performance.
In summary, process optimization, encompassing identifying inefficiencies, streamlining procedures, leveraging technology, and continuous monitoring, directly contributes to a higher "pauda score." A well-optimized process consistently performs at a superior level, reflected by a favorable numerical value for the metric. Effective implementation of these optimization strategies contributes to the advancement and improvement of any process, measured directly by the "pauda score."
6. Quality Improvement
Quality improvement initiatives are intrinsically linked to the "pauda score." A high "pauda score" typically signifies a process or system operating at a superior level, consistently producing high-quality outputs. Conversely, a low "pauda score" often points to areas needing improvement within the procedures and processes. Quality improvement, therefore, is a critical component in achieving and maintaining a high "pauda score." By proactively addressing identified weaknesses and implementing corrective actions, organizations can elevate their "pauda score" and ensure consistent high-quality performance.
Consider a manufacturing setting. A consistently low "pauda score" might indicate high defect rates. Implementing quality improvement programs, such as enhanced training for production staff, improved equipment maintenance schedules, or revised quality control procedures, directly addresses the root causes of defects and consequently improves the "pauda score." In a customer service environment, a low "pauda score" could suggest high customer complaint rates. Quality improvement might involve enhanced employee training in communication and problem-solving, streamlined complaint resolution processes, or the implementation of customer feedback systems. These strategies, focused on customer satisfaction, directly translate into a higher "pauda score." In project management, a low "pauda score" can indicate delays or cost overruns. Implementing methodologies like Agile development, comprehensive risk management plans, or robust project monitoring systems can result in improved project outcomes and lead to a higher "pauda score." In each instance, quality improvement efforts directly impact the "pauda score" by bolstering overall process efficacy and the consistency of high-quality output.
In conclusion, quality improvement directly influences the "pauda score." Quality improvement initiatives are not merely beneficial additions but essential components in achieving and maintaining a high "pauda score." By effectively addressing areas requiring improvement and consistently implementing quality control measures, organizations can systematically enhance their performance, measured by the numerical value of the "pauda score." Understanding this connection allows for a strategic approach to continuous improvement, ultimately ensuring sustained excellence in performance metrics. The "pauda score," then, becomes a valuable tool to measure the effectiveness of quality improvement initiatives, providing tangible evidence of their positive impact on processes and overall operational performance.
Frequently Asked Questions about the "pauda score"
This section addresses common queries regarding the "pauda score." Understanding this metric's components and applications is essential for accurate interpretation and effective use.
Question 1: What exactly does the "pauda score" measure?
The "pauda score" quantifies performance within a specific context. This context might be a production process, a customer service interaction, or a project's progress. Crucially, the metric assesses a predefined set of criteria, often including quality, efficiency, and timeliness. The specific components evaluated depend on the intended application. For example, in manufacturing, the "pauda score" might be influenced by defect rates and production output. In a customer service setting, it could assess resolution times and customer satisfaction ratings.
Question 2: How is the "pauda score" calculated?
Calculation methodologies vary depending on the application. Generally, data relevant to the pre-defined criteria are collected and analyzed. These data points are then weighted and combined using established formulas to arrive at a numerical "pauda score." The specific data, weights, and formulas are tailored to the specific process or system being evaluated.
Question 3: What are the benefits of utilizing the "pauda score"?
Utilizing the "pauda score" offers several advantages. It provides a standardized metric for evaluating performance, facilitating comparison across different time periods or similar entities. The objective nature of the score allows for easy tracking of improvements and the identification of areas requiring attention. Furthermore, the "pauda score" often aids in the continuous improvement of processes by pinpointing specific areas for optimization.
Question 4: How can organizations interpret a low "pauda score"?
A low "pauda score" indicates a need for assessment and potential improvement within the evaluated system or process. A thorough examination of collected data is crucial to understanding the reasons behind the low score. This might involve identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or areas where quality control measures need strengthening. Analyzing these factors is vital for developing targeted interventions aimed at improving the metric.
Question 5: Can the "pauda score" be applied in various industries?
Yes, the "pauda score" concept is adaptable across diverse industries. However, the specific criteria used for evaluation must be tailored to the particular industry's context and objectives. Whether in manufacturing, healthcare, customer service, or project management, the ability of the "pauda score" to offer a quantifiable measure of performance remains consistent, but the specific data inputs need to reflect the relevant metrics of the industry.
Understanding the fundamentals of the "pauda score," including its calculation, application, and interpretation, is crucial for effective process improvement. The subsequent sections will delve into practical applications and case studies of the "pauda score." This will further clarify its relevance and benefits in diverse operational contexts.
Conclusion
The "pauda score" serves as a critical performance metric, offering a quantifiable representation of process efficiency and quality. Its application across various sectors, from manufacturing to project management, underscores its versatility. Key elements contributing to a robust "pauda score" include meticulous performance evaluations, data-driven insights, targeted process optimization, and the implementation of continuous quality improvement initiatives. Benchmarking against established standards provides context, enabling organizations to identify areas for improvement and maintain competitive advantage. The successful utilization of the "pauda score" hinges on the thoroughness and accuracy of data collection, analysis, and subsequent interpretation. This metric facilitates proactive problem-solving and continuous progress towards optimal operational performance. Ultimately, the "pauda score" provides a valuable tool for objective performance assessment and strategic decision-making.
The effective application of the "pauda score" necessitates a profound understanding of its underlying principles. Organizations must meticulously define the scope and criteria of evaluation to ensure meaningful and accurate results. Continuous refinement of methodologies and data analysis procedures is essential to maintain the metric's relevance and reliability. As industry standards evolve and processes become more complex, the "pauda score" remains a vital mechanism for assessing performance, driving improvements, and ultimately achieving sustained excellence.
![[PDF] Critical evaluation of the PADUA score in a retrospective](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/9be2e9c8d1c8546719906a910c0c4b0aa33bfbf3/3-Table1-1.png)
Detail Author:
- Name : Kevon Wisoky
- Username : janie30
- Email : delia.walter@dicki.com
- Birthdate : 1986-04-12
- Address : 370 Palma Landing Suite 444 Schultzland, FL 15558
- Phone : +1-947-689-6675
- Company : Bernier, Crona and Lubowitz
- Job : Production Worker
- Bio : Doloribus voluptatem hic modi molestiae ea. Deserunt id vitae ex qui ex facilis. Officia non ullam voluptatem voluptatem sed ratione exercitationem.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/jazmin_dev
- username : jazmin_dev
- bio : Excepturi aut deleniti pariatur non earum odit.
- followers : 5670
- following : 534
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/jazmin4645
- username : jazmin4645
- bio : Delectus repellat enim et quaerat. Animi inventore debitis rerum. Et rem totam et labore facere.
- followers : 5751
- following : 1930
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@jazmin_xx
- username : jazmin_xx
- bio : Aspernatur qui enim nemo iusto temporibus.
- followers : 6850
- following : 14
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/jazmin_dev
- username : jazmin_dev
- bio : Dolor dignissimos vitae et dolores soluta. Velit sint in repudiandae saepe omnis itaque. Hic officia vitae nesciunt unde.
- followers : 5108
- following : 1884
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/jjacobson
- username : jjacobson
- bio : Architecto alias aliquam sapiente minima assumenda et autem voluptatem.
- followers : 6196
- following : 2303