What does this spatial representation offer regarding understanding and navigating a specific community? A comprehensive visual representation of a community's characteristics holds significant value in a multitude of applications.
This document likely refers to a geographical representation depicting various attributes of a community, such as demographics, socioeconomic factors, infrastructure, and other key elements. An example would be a map showcasing housing density, income levels, and the distribution of educational institutions within a defined area. This kind of map provides a visual snapshot of the community's composition and potential challenges or opportunities.
Such a map is crucial for community planning and development. It allows for informed decision-making regarding resource allocation, infrastructure improvements, and social service delivery. By visually identifying patterns and disparities, effective strategies can be formulated. Further, the historical context of the community's evolution can be explored through the change in the map over time. This visual data is also valuable in understanding community dynamics and potential areas for growth or intervention.
Moving forward, further analysis can be performed using this type of spatial representation. For example, areas of high concentration of certain demographics may be further investigated to understand the factors influencing those trends. The map's insights can be foundational to community engagement and collaborative initiatives to ensure the well-being of its residents.
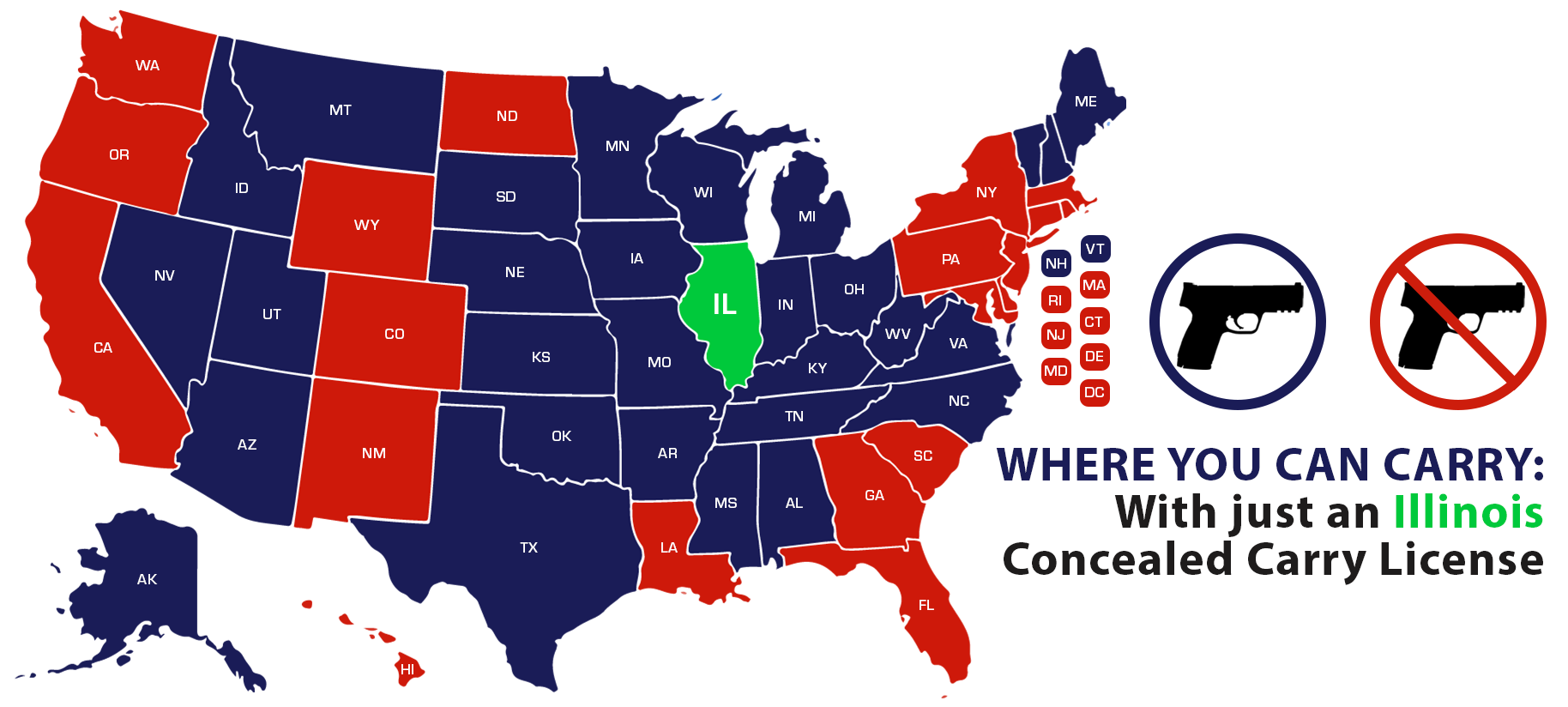
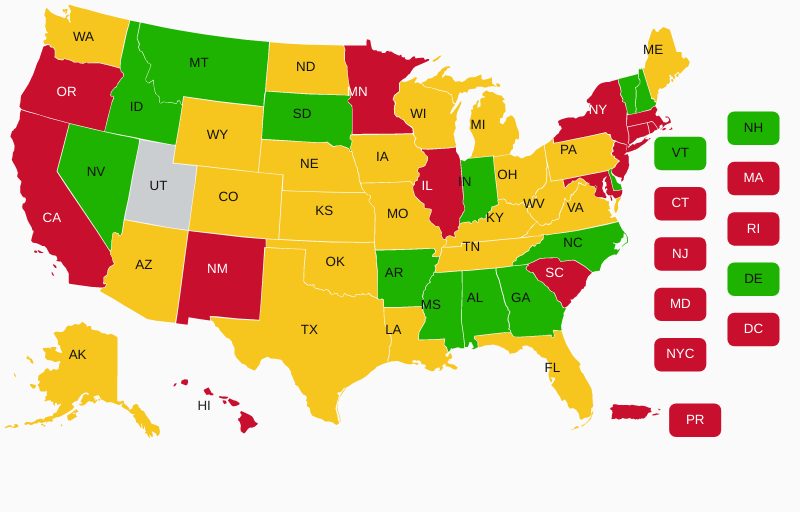
USCCA Map
Understanding the spatial representation of crucial community attributes is essential for effective planning and development. This map, likely a visual representation of demographics, infrastructure, and other community characteristics, holds significant value.
- Geographic Scope
- Data Visualization
- Community Attributes
- Resource Allocation
- Trend Analysis
- Stakeholder Engagement
The geographic scope of the map defines the area of study, while data visualization portrays the collected community attributes. This map allows for the identification of key demographics, which informs resource allocation strategies. Analyzing trends in housing patterns or population density helps understand community evolution. The map facilitates stakeholder engagement by presenting data in an accessible format, thereby fostering collaboration and informed decision-making. Understanding specific attributes, such as unemployment rates, can reveal potential intervention areas, leading to targeted support. For instance, a high concentration of low-income families identified on the map would prompt targeted programs for improving economic stability within that region.
1. Geographic Scope
The geographic scope of a community-focused map, akin to a USCCA map, directly dictates the data's applicability and the insights it can offer. Defining the area of analysis is fundamental; a map encompassing a small neighborhood will yield different results than one covering a larger metropolitan region. The boundaries determine the range of data collection, impacting its relevance to any specific planning or intervention efforts.
- Defining the Study Area
Precisely defining the geographic boundaries is paramount. This involves meticulous delimitation of neighborhoods, counties, or even larger regions depending on the analytical objectives. Clear demarcation ensures data relevance and avoids skewed conclusions based on overly broad or narrow scopes. Examples include defining a specific city ward for a local development project or a state for assessing statewide educational disparities.
- Relevance to Specific Needs
The geographic scope is not arbitrary; it should align with the specific concerns or initiatives the map seeks to address. A map focused on addressing overcrowding in a particular school district would necessitate a narrower scope than one examining broader regional economic trends. By linking scope to objectives, the analysis remains targeted and actionable.
- Data Collection Considerations
The geographical scope affects data collection efforts. Obtaining comparable data from numerous sources within a defined boundary might require specific data collection methods. Sampling and data availability might be impacted based on the size and complexity of the area. A map covering a large area might rely on aggregated data from multiple sources, while a smaller scope could use more granular information.
- Impact on Analysis and Recommendations
The scope fundamentally alters the analysis. A small scope could reveal neighborhood-specific issues, whereas a larger scope might showcase broader regional patterns. Recommendations arising from the analysis will directly correlate with the map's geographic bounds, with solutions tailored to the specific area investigated.
In summary, the geographic scope of a community map profoundly influences the comprehensiveness and applicability of the analysis. By carefully considering and defining the geographical boundary, the map can effectively highlight pertinent trends, offer actionable insights, and generate impactful recommendations for targeted interventions within specific geographic areas.
2. Data Visualization
Data visualization plays a critical role in the effectiveness of a community-focused map, such as a hypothetical "USCCA map." Visual representations of data transform complex information into easily digestible formats. This allows for quick identification of patterns, trends, and disparities within a community. Effective visualization facilitates understanding of geographical distributions, enabling better analysis of socioeconomic characteristics, infrastructure availability, and other pertinent data points. For instance, a map displaying housing affordability rates using different color gradients allows immediate comprehension of wealth disparity across various neighborhoods. Clearer understanding of this data leads to targeted resource allocation for areas requiring enhanced support.
The choice of visualization techniques significantly impacts the clarity and utility of the map. Choropleth maps, for example, effectively depict variations in data across geographic regions by utilizing color gradations. Scatter plots can highlight correlations between different variables, such as income and education levels. Utilizing interactive elements, like clickable markers or hover-over details, allows for greater depth of analysis and enables users to explore particular areas of interest in more detail. A clear example would be a map illustrating crime rates overlaid with demographics, offering policymakers the opportunity to pinpoint high-crime regions and potential correlations for improved intervention strategies.
In conclusion, robust data visualization is integral to a community-focused map. It transforms raw data into actionable insights by visually presenting complex information in a clear, accessible format. Effective visual representations are essential for community understanding and are a crucial part of any strategic planning initiative. The strength of this visualization approach lies in its ability to facilitate informed decision-making and targeted interventions at the community level by allowing for quick comprehension of trends and disparities. A thoughtfully designed visualization ensures the maps utility and facilitates proactive responses to challenges within the community.
3. Community Attributes
A comprehensive understanding of community attributes is essential for effective planning and resource allocation. A document like a hypothetical "USCCA map" relies on these attributes to provide a nuanced representation of a community. These attributes, encompassing various aspects of community life, are crucial for interpreting the map and formulating targeted strategies for improvement or intervention.
- Demographics
Demographic characteristics, such as age distribution, ethnic composition, and household income, are fundamental components of community understanding. A map might illustrate areas with a high concentration of senior citizens or specific ethnic groups, potentially revealing distinct needs for social services or infrastructure. These insights are vital for tailoring services and resources to cater to the specific demands of the community.
- Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors, including income levels, employment rates, and poverty levels, significantly impact a community's well-being. A map highlighting these factors can reveal areas with high rates of poverty or unemployment, prompting targeted initiatives for economic development and job creation. These insights are vital for policymakers and community organizations aiming to address economic disparities.
- Housing and Infrastructure
The distribution of housing types, quality, and access to essential services like transportation and healthcare form crucial components of a community's infrastructure. A map can depict areas with limited access to affordable housing or inadequate infrastructure, directing attention to addressing these issues. Such insights are vital for planning equitable access to essential services and improving the overall quality of life for community members.
- Education and Healthcare Access
The availability and quality of educational opportunities and healthcare facilities are crucial community attributes. A map can illustrate areas lacking adequate schools, access to quality education, or primary care facilities. These disparities directly impact community members' long-term well-being. Understanding these attributes is essential for planning community-based initiatives focused on improving educational opportunities and enhancing healthcare access.
In essence, a "USCCA map" draws upon these various community attributes. By presenting these attributes geographically, the map facilitates a more thorough and actionable understanding of the community's composition. This, in turn, can inform decisions for planning, resource allocation, and the design of targeted interventions aimed at enhancing the overall well-being and quality of life for the community members.
4. Resource Allocation
Effective resource allocation is intrinsically linked to the utility of a community-focused map like a hypothetical "USCCA map." The map's data, depicting community attributes, directly informs strategic decisions regarding resource distribution. Understanding the spatial distribution of various needs, from educational facilities to healthcare access, enables targeted investments and prevents inequitable resource allocation. For instance, a map illustrating high concentrations of low-income families coupled with inadequate access to quality schools necessitates focused investment in educational programs and infrastructure improvements in those areas.
The practical significance of this connection is substantial. Consider a scenario where a community map reveals a disparity in access to internet infrastructure. This visual data empowers policymakers to prioritize the allocation of funds for expanding internet access in underserved areas. Similarly, areas with disproportionately high rates of childhood poverty, identified on a map, prompt focused efforts on early childhood education programs. This targeted allocation of resources, based on the map's insights, directly addresses community needs and fosters more equitable outcomes. Real-world examples abound. Cities have used similar data-driven methodologies to allocate resources for combating crime in specific neighborhoods or expanding affordable housing options where demand is high and supply is limited. The resulting improvements in community well-being underscore the vital role of the map-driven resource allocation decisions.
In conclusion, a "USCCA map" provides a foundational framework for informed resource allocation decisions. By visually representing crucial community attributes, the map facilitates the identification of disparities and needs, leading to more targeted and effective strategies for resource deployment. The practical application of such insights leads to more equitable distribution of resources, enhanced community well-being, and ultimately, improved quality of life. However, challenges remain in the accuracy and accessibility of data, and ongoing evaluation of the effectiveness of resource allocation strategies based on map analysis is essential.
5. Trend Analysis
Trend analysis is a critical component of a comprehensive community map, like a hypothetical "USCCA map." It allows for the identification of patterns and shifts in community characteristics over time. This temporal analysis is vital for understanding evolving needs and potential future challenges. For example, a map might reveal a gradual increase in the elderly population in a specific region. This trend, detected through analysis of census data over a number of years, suggests a potential need for expanded senior services and supports in that area. Understanding this pattern facilitates proactive planning, instead of reacting to immediate crises.
The importance of trend analysis lies in its capacity to project future needs and anticipate potential issues. Consider a map illustrating rising unemployment rates in a particular community sector. Analyzing this trend, perhaps correlated with the closure of a major employer, enables community leaders to proactively implement job training programs or economic development initiatives. By identifying emerging trends, communities can mitigate negative impacts and foster proactive growth. Historical data on housing availability and construction trends, for instance, provides insight into the evolving housing market and potential future housing demands.
Successful trend analysis, as an integral part of a community map, relies on consistent data collection and a clear understanding of historical context. However, challenges exist. Accurate data collection and analysis can be complex. Maintaining consistent data collection methodologies throughout different time periods is crucial for reliable comparisons. Without this consistency, the results of trend analysis become unreliable. Furthermore, interpreting trends and projecting future needs requires careful consideration of external factors that may influence the community's trajectory, such as economic conditions, national policies, or technological advancements. Despite these challenges, effective trend analysis using a community map like the hypothetical "USCCA map" offers invaluable insights for informed decision-making, resulting in more effective and responsive community development efforts. Community leaders, policymakers, and stakeholders can use this information to proactively address future needs and support long-term growth and sustainability.
6. Stakeholder Engagement
Effective stakeholder engagement is crucial for the successful implementation of any community-focused initiative, including those leveraging insights from a community map (hypothetical "USCCA map"). Engagement fosters a collaborative environment where diverse perspectives are considered, leading to more comprehensive and sustainable solutions. A maps utility is maximized when stakeholders are actively involved in understanding and interpreting the presented data.
- Diverse Perspectives and Input
Involving a broad spectrum of stakeholderscommunity members, local businesses, government representatives, and non-profit organizationsensures a comprehensive understanding of the communitys needs and priorities. This ensures that the map's insights are relevant and actionable. Diverse perspectives on issues like affordable housing, access to education, or community safety lead to well-rounded recommendations for improvement. For example, a local business owner might offer unique insights into job market demands, while a community activist might highlight critical concerns regarding public safety.
- Shared Understanding of the Data
Transparent communication and interpretation of the map's data facilitate shared understanding. Workshops, presentations, and community forums are valuable tools for ensuring that all stakeholders comprehend the map's visual representations and associated implications. This process builds trust and increases buy-in for subsequent actions based on the map's findings. A common understanding reduces misinterpretations and builds a stronger foundation for collaborative problem-solving.
- Co-Creation of Solutions
Stakeholder engagement fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility. Active participation in identifying challenges and generating potential solutions strengthens community-led initiatives. This co-creation process leads to a stronger sense of commitment amongst stakeholders, ensuring that the communitys needs are deeply embedded in the development and implementation of solutions derived from a community map. Through brainstorming sessions and collaborative projects, stakeholders can work together to develop practical strategies.
- Measurable Outcomes and Accountability
Establishing clear metrics for assessing the effectiveness of initiatives, directly informed by the map's data, ensures accountability and transparency. Stakeholder engagement, through regular evaluation and feedback mechanisms, ensures that these efforts remain aligned with community needs. This ongoing monitoring of outcomes and participation allows for adjustments and improvements throughout the process.
Ultimately, stakeholder engagement ensures that a community map, like a hypothetical "USCCA map," is not merely a static document but a dynamic tool for community development. Active participation by diverse groups of stakeholders guarantees that the data informing the map drives tangible improvements in the community, leading to positive outcomes and greater community cohesion. Active, informed participation ensures the map becomes more than just a visualization of current conditions but a roadmap for future progress and prosperity.
Frequently Asked Questions about Community Maps
This section addresses common inquiries regarding community maps, particularly those focused on visualizing community attributes. These maps provide a valuable tool for understanding and addressing community needs.
Question 1: What is the purpose of a community map, such as a hypothetical "USCCA map"?
Community maps, including a hypothetical "USCCA map," aim to visually represent key attributes of a community. This includes demographics, socioeconomic factors, infrastructure, and other relevant elements. The purpose is to facilitate a comprehensive understanding of the community's composition, allowing for informed decision-making in planning and resource allocation.
Question 2: How are the data for a community map collected and compiled?
Data for community maps often originate from various sources, including census data, surveys, local government records, and other publicly accessible information. Careful consideration of data accuracy and reliability is crucial. Methods for data aggregation and visualization depend on the map's specific objectives and intended audience.
Question 3: What are the limitations of using community maps for decision-making?
While community maps offer valuable insights, limitations exist. Data limitations, potential biases in data collection, and the potential for misinterpretation of visual representations should be acknowledged. Maps alone do not provide solutions; they are a tool to facilitate discussion and guide further analysis.
Question 4: How can stakeholders contribute to the development or improvement of a community map?
Active engagement of stakeholders is essential. Community members, local businesses, government representatives, and non-profit organizations can provide valuable insights, feedback, and data. Open forums and workshops allow for diverse perspectives to influence the creation of a relevant and effective map.
Question 5: How can organizations use community map information effectively?
Organizations can use community map information to identify areas needing targeted interventions, allocate resources strategically, and understand potential challenges. Specific projects like infrastructure improvements, educational initiatives, or social programs can benefit from using community maps to ensure solutions are grounded in a community's unique needs.
In conclusion, community maps, like the hypothetical "USCCA map," serve as powerful tools for understanding and addressing community needs. However, acknowledging limitations, fostering stakeholder engagement, and utilizing data effectively are crucial for successful implementation and impactful outcomes.
Moving forward, exploring the practical application of community mapping techniques will be discussed in the subsequent section.
Conclusion
This exploration of a hypothetical "USCCA map" underscores the significance of comprehensive community analysis. The article highlights the crucial role of geographical representation in understanding community attributes, including demographics, socioeconomic factors, infrastructure, and access to essential services. The exploration demonstrates how such maps facilitate informed resource allocation, enabling targeted interventions to address specific community needs. Key considerations, such as geographic scope, data visualization, and stakeholder engagement, were emphasized. Trend analysis, essential for anticipating future challenges and opportunities, was also discussed. Ultimately, the article argues for the strategic application of these maps as crucial tools for community development. Their utility hinges on meticulous data collection, effective visualization techniques, and active engagement of relevant stakeholders.
Moving forward, the successful implementation of community mapping projects relies on maintaining data accuracy and accessibility, and on the commitment of community members, policymakers, and organizations to collaborative problem-solving. The creation and utilization of these maps necessitate ongoing evaluation to ensure their continued relevance and efficacy in supporting targeted interventions and fostering community well-being. The future of effective community development hinges on the insightful use of these vital analytical tools.
Detail Author:
- Name : Thad Mante
- Username : koss.lilly
- Email : kayli.okon@powlowski.com
- Birthdate : 1987-07-28
- Address : 828 Talia Stream Suite 466 Dickinsonberg, HI 48947-2585
- Phone : 952-734-7849
- Company : Bradtke, Konopelski and Champlin
- Job : Custom Tailor
- Bio : Vel nobis unde consequatur vero amet. Quas reprehenderit sunt possimus. Tempore omnis est hic vel reiciendis non veritatis quia. Cupiditate labore in et delectus sapiente facere.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/julie1053
- username : julie1053
- bio : Nostrum sit laborum recusandae ullam. Iusto quia nemo ut nesciunt. Officia sunt neque qui cumque sapiente dolores.
- followers : 5838
- following : 893
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/julie_schimmel
- username : julie_schimmel
- bio : Ipsa voluptatem earum asperiores magnam dolor illum. Alias eius ut quos et molestiae vero cumque.
- followers : 4948
- following : 1009